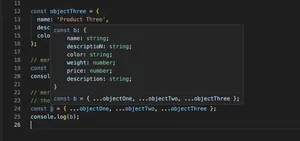
In TypeScript, a powerful and popular static type-checker for JavaScript, we often encounter scenarios where an object’s properties may not always be mandatory. In such cases, we leverage optional properties to keep our code flexible and robust. This comprehensive tutorial with code examples will guide you through the concept of optional properties in TypeScript.
Understanding Optional Properties
In TypeScript, optional properties are those properties that are not obligatory in an object’s structure. To denote a property as optional, we use a question mark ? right after the property’s name. This gives us the ability to create flexible object structures where certain properties may or may not be present.
type User = {
name: string;
age?: number;
}In the code snippet above, age is an optional property in the User object.
Creating Optional Properties
There are several ways to create optional properties in TypeScript. They can be defined in type aliases, interfaces, and classes.
Type Aliases
type Person = {
name: string;
age?: number;
}Classes
class Person {
name: string;
age?: number;
constructor(name: string, age?: number) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}In each of these examples, the property age is optional.
Interfaces
Optional properties in interfaces are defined using the same syntax as in type aliases and classes. Here’s an example:
interface Person {
email: string;
name?: string;
phone?: string;
}In this interface, name and phone are optional properties.
Dealing with Undefined
When accessing an optional property that has not been assigned a value, TypeScript returns undefined. This is expected behavior as the property is not required to have a value.
interface Person {
name: string;
age?: number;
}
let person: Person = {
name: "John Doe"
}
console.log(person.age) // undefinedHowever, TypeScript also allows us to explicitly assign an undefined value to an optional property.
interface Person {
name: string;
age?: number;
}
let person: Person = {
name: "John Doe",
age: undefined
}
console.log(person.age) // undefinedConfiguring ExactOptionalPropertyTypes
By using the exactOptionalPropertyTypes option in the tsconfig.json file, we can prevent TypeScript from assigning undefined to an optional property. This option is part of the compilerOptions section.
{
"compilerOptions": {
"exactOptionalPropertyTypes": true,
"strictNullChecks" : true
}
}When this option is enabled, trying to assign undefined to an optional property will result in a compiler error.
Utilizing Partial Utility Type
TypeScript provides utility types that allow us to construct new types from existing ones. The Partial utility type is one such resource. It converts all properties of a given type to optional.
interface Person {
name: string;
address: string;
age: number;
}
let person: Partial<Person> = {}In this example, the Partial utility type is used to make all properties of the Person interface optional.
Function with Optional Properties
Optional properties can also be used in functions. In the following example, the printInfo function accepts a Person object as a parameter, and it prints the information of the person.
interface Person {
email: string;
name?: string;
phone?: string;
}
function printInfo(person: Person) {
console.log('Email:', person.email);
if (person.name) {
console.log('Name:', person.name);
}
if (person.phone) {
console.log('Phone number:', person.phone);
}
}In TypeScript, both optional parameters and parameters of type number | undefined allow for the argument to be omitted. However, a function with an optional parameter allows the function to be called without any arguments, whereas a function expecting a parameter of type number | undefined requires at least one argument.
Conclusion
Mastering optional properties in TypeScript can significantly improve your coding skills and open up new ways to handle data structures. As we’ve seen, optional properties offer flexibility and robustness when defining object structures, allowing for properties to be absent when they’re not needed. By using optional properties, we can write cleaner, more maintainable code that can handle a variety of data scenarios.